Supination
Description
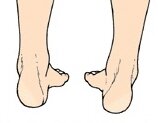
Supination is a turning inward of the foot at the ankle, so that one has a tendency to walk on the outer border of the foot. |
|
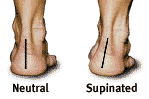
Chief Diagnostic Sign: You can test for supination by looking at the leg and foot from the back. Normally you can see the Achilles tendon run straight down the leg into the heel. If the foot is supinated, the tendon will run straight down the leg, but when it lies on the heel it will twist inward. This makes the outer ankle bone appear more prominent than the inner ankle bone.
Because supination is a twisting of the foot, all of the muscles and tendons that run from the leg and ankle into the foot will be twisted. If left untreated, supination may be the cause of heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, hallux limitus and rigidus, ball of foot pain (metatarsalgia), shin splints, high and painful arches, and eventually knee, hip, and lower back pain. Supination can also predispose to ankle sprains due to the excess stress applied to the lateral ankle tendons and ligaments.
Causes
The most common cause of supination is genetics — we generally are born with this biomechanical defect. The second most common cause is due to the way our feet were positioned in the uterus while we were developing; this is called a congenital defect. In either instance, the following occurs in our feet during our development:
The muscles, ligaments, and other soft tissue structures that hold our foot bones together at the joints become tighter than normal. When the bones are held too rigidly in place, they cannot move properly, and the foot gradually turns inward at the ankle, causing the outer ankle bone to appear more prominent. The bones of the foot, and the foot itself, moves in this direction because the tendons that attach to the bones on the inner side of the foot become tighter that those that attach to the outer side of the foot. As we develop, the muscles and ligaments accommodate to this abnormal alignment. By the time growth is complete, the supinated foot is usually: abnormally rigid, high arched, and its inner border appears raised so that as you step down you do not come down equally across the entire foot; instead, you come down mostly on the outer border of the foot. |
|
Symptoms
Due to the excessive tightness of the soft tissues of the foot, the bones of the feet shift. When this occurs, the muscles that attach to these bones must also shift, or twist, in order to reach the bones they attach to. The strongest and most important muscles that attach to our foot bones come from our lower leg. So, as these muscles course down the leg and across the ankle, they must twist to maintain their proper attachments in the foot. This twisting of these muscles will cause: shin splints, generalized tendonitis, fatigue, muscle aches, and pains, cramps, and loss of muscular efficiency (reducing walking and running speed and endurance). Another early symptom is often abnormal shoe wear and difficulty finding comfortable shoes due to lateral stress on the outer ankle.
The problems we see in the feet which may be due to supination include: ball of foot pain (metatarsalgia), deep and painful calluses, bunions, hammertoes, heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, and high arches that are painful when not properly supported.
Treatment
-
Children: If supination is diagnosed before the age of five it can usually be treated in such a manner that the bones and joints will be aligned properly as growth continues. This allows the muscles of the leg to enter the foot without twisting. With proper and early treatment, the foot may not turn in at the ankle, and the child’s gait will improve. Treatment for supination in children may include: night braces, custom-made orthotics, and exercises. These treatments usually continue until growth is complete, and then the adult may need to wear custom-made orthotics to prevent the supination from returning (the foot, as every other part of our body, tends to return to its original form if preventive measures are not taken). One side note: occasionally, pediatricians may wait too long, hoping that the child will “outgrow” the problem. By the time they realize that the child’s feet will not improve, it is too late to change the foot. In these cases, custom-made orthotics is used to prevent the supination from becoming worse.
-
Adults: Most foot and ankle specialists agree that the most effective non-surgical treatment for supination is custom-made orthotics.
How custom-made orthotics for supination work:
-
Supination forces us to bear most of our weight on the outer border of our feet. Custom-made orthotics gently redistributes the weight so that the entire foot bears its normal share of weight with each step we take. The foot will not twist in at the ankle, but will strike the ground normally when the orthotics is used. This action of the custom-made orthotics will help to prevent: shin splints, generalized tendonitis, fatigue, muscle aches, and pains, cramps, and loss of muscular efficiency (reducing walking and running speed and endurance).
-
Custom-made orthotics support not only the arch as a whole, but each individual bone and joint that forms the arch. It is not enough to use an over-the-counter arch support, as these generic devices will not provide the proper support to each specific structure of the arch and foot. Each high arched and supinated foot is different, and the height of the arch varies from individual to individual. The only way to provide the support that you may need is with a custom-made device. This action of the custom-made orthotic can help to prevent: ball of foot pain (metatarsalgia), deep and painful calluses, bunions, hammertoes, heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, and high arches that are painful when not properly supported.
-
Custom-made orthotics will reduce the twisting of the leg muscles as they enter the foot, by maintaining a normal alignment of the bones and joints of the foot. If the bones and joints are aligned properly, by reducing the supination, the muscles can run straight to their attachments in the foot, without twisting to get to these bones. This action of custom-made orthotics will reduce Achilles tendonitis; shin splints; ankle, knee, hip, and lower back pain; and leg cramps. This action will also allow the leg muscles to work more efficiently, thus allowing you to walk and run with less effort.
-
With every step we take, we place at least half of our body weight on each foot (as we walk faster, or run, we can exert more than twice our body weight on each foot). As this amount of weight is applied to each foot there is a significant shock passed on to our body. Custom-made orthotics will absorb some of this shock, helping to protect our feet, ankles, knees, hips, and lower back. Our custom-made orthotics for supination are constructed of thin, comfortable, modern shock absorbent materials. These materials compress as you place your weight on the orthotic, thus absorbing the shock of each step, rather than passing on these shocks to the foot, leg, and spine. When you remove your weight from the orthotic, the orthotic returns to its original shape and height. This occurs because the materials we use have a”memory,” and can remember their original shape and height, and return to it. These materials will comfortably keep the foot in its proper alignment, relieving the supination and its symptoms, while helping to prevent further associated problems from occurring.
Based on impressions of your feet and information you provide on a comprehensive self-examination form, we can design and construct a pair of orthotics that will help to reduce your supination, muscle imbalances, foot and leg pain and fatigue, and foot abnormalities. These orthotics will fit into any shoe with a heel height up to 1 1/2 inches.